
CS155: Homework #1
Spring 2023
Due: Thursday, Apr. 27, 11:59pm PT
Problem 1: Jump Oriented Programming (JOP)
Elizabeth is attacking a buggy application. She has found a vulnerability that allows her to control the values of the registers ecx, edx, and eip, and also allows her to control the contents of memory locations 0x9000 to 0x9014. She wants to use return-oriented programming, but discovers that the application was compiled without any ret instructions! Nonetheless, by analyzing the application, she learns that the application has the following code fragments (gadgets) in memory:
0x3000: add edx, 4 ; edx = edx + 4
jmp [edx] ; jump to *edx
0x4000: add edx, 4 ; edx = edx + 4
mov eax, [edx] ; eax = *edx
jmp ecx ; jump to ecx
0x5000: mov ebx, eax ; ebx = eax
jmp ecx ; jump to ecx
0x6000: mov [eax], ebx ; *eax = ebx
... ; don't worry about what happens after this
Show how Elizabeth can set the values of the registers and memory so
that the vulnerable application writes the value 0x2222
to memory address 0x8888.
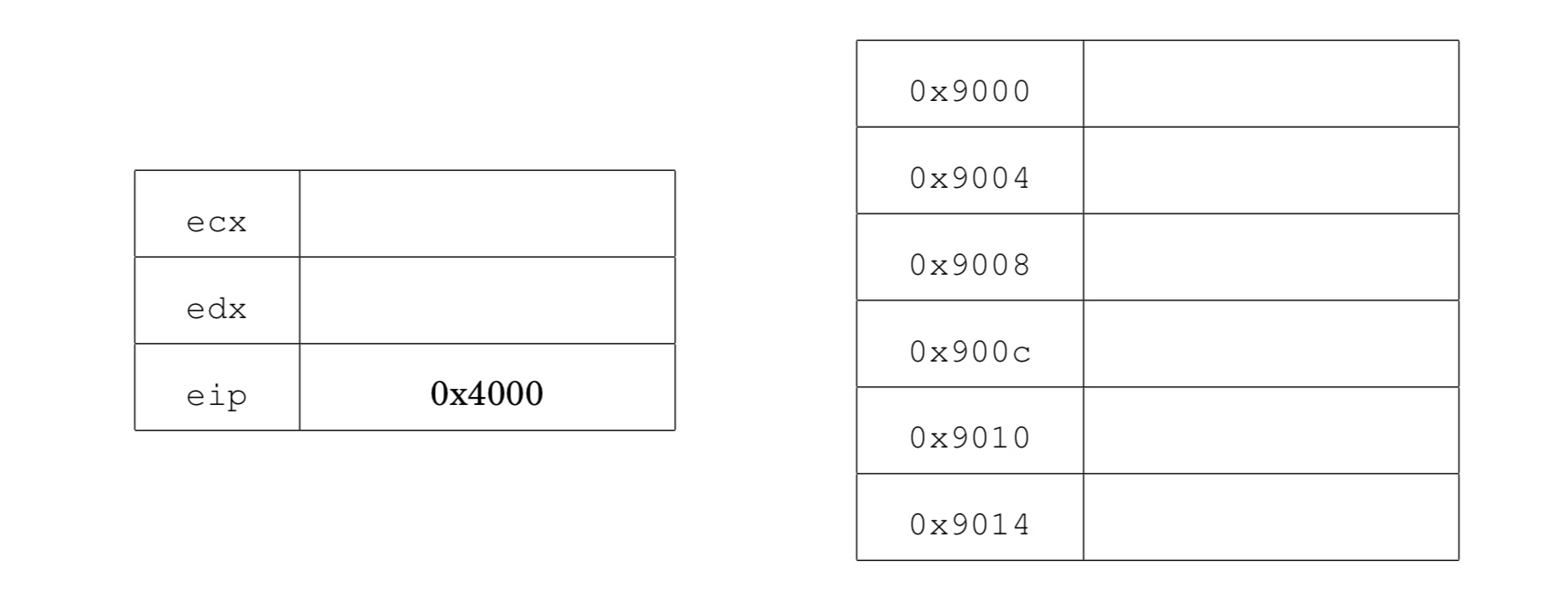
Recall that eip is the instruction pointer. It holds the address of the next instruction to execute. ecx and edx are general purpose registers.
Problem 2: Stack canaries
-
Recall that when GCC is used to compile a C program with the -fstack-protector flag,
the compiler places a stack canary in (almost) every stack frame, and re-orders the local variables.
This flag implements a variant of ProPolice discussed in slide 20 in lecture 3.
Write a short sample C program that takes command line input and is vulnerable to a stack smashing attack
(i.e., an attack the causes the return address on the stack to be overwritten)
even when the program is compiled using GCC
with the -fstack-protector flag enabled.
Hint: your code could contain a structure that is allocated on the stack, and the structure contains two fields: a pointer and a string. You may assume that the fields of the structure are allocated consecutively on the stack, with the first field allocated at a lower memory address than the second field. An overflow of the string buffer will overwrite the pointer in the structure. Your code should make it possile for the attacker to use that to overwrite entries on the stack. - Suppose the OS marks all stack memory pages as non-executable. Can stack smashing be used to mount a control hijacking attack? If so, briefly explain how. If not, explain why not.
Problem 3: Integer underflow vulnerability
Consider the following simplified code that was used earlier this year in a widely deployed router:
uint32_t nlen, vlen; /* values in 0 to 2^32-1 */
char buf[8264];
nlen = 8192;
if ( hdr->nlen <= 8192 )
nlen = hdr->nlen;
memcpy(buf, hdr->ndata, nlen);
buf[nlen] = ':';
vlen = hdr->vlen;
if (8192 - (nlen+1) <= vlen ) /* DANGER */
vlen = 8192 - (nlen+1);
memcpy(&buf[nlen+1], hdr->vdata, vlen);
buf[nlen + vlen + 1] = 0;
If hdr->ndata = "ab" and hdr->vdata = "cd"
then this code is intended to write "ab:cd" into buf.
Suppose that the attacker has full control of the contents of hdr.
Explain how this code can lead to an overflow of the local buffer buf.
Problem 4: Privilege Escalation
After poking around your Unix-based system as the user laura, you stumble to find the following file in /sbin:
-rwsrwxr-x 1 root laura 234K Apr 01 21:32 pingWhat's the potential security vulnerability? How might you use this file to escalate your privileges to root? (Assume that ping does not have any vulnerabilities in its implementation.)
Modern versions of Linux try to prevent this security escalation. What is the defensive behavior? Hint: try creating a file with these permissions on your VM from Project 1, orchestrating your attack, and seeing what happens.
Problem 5: Android Isolation
In Android, each app runs in a separate process using a separate user id. From a security standpoint, what is the advantage of assigning separate UIDs instead of using the same UID for all apps?Problem 6: Reducing executable permissions
After discovering a vulnerability in the passwd utility, the Linux developers have decided that it is too dangerous to conintue to run the utility as root (through setuid). Unfortuantely, there's no Linux capability that lets a process specifically edit /etc/shadow, the file that Linux uses to store password data.
- The kernel developers have asked you to devise a new mechanism where the passwd command no longer runs as root, but users can only change their own password and can't change any other users' passwords. Your solution can't change the Linux kernel itself (e.g., introduce a new capability), but the developers have created a new service account passwd that you can use. You can change the ownership, permissions, or setuid bit on any files, but you should note the new configurations in your solution.
- What's the worst damage that an attacker can do if a new code exploit vulnerability were to be found in passwd after your proposed fix?
- Does changing who runs the passwd utility meaningfully increase the security of the system? Why or why not? Hint: Think about the contents of the /etc/shadow file.
Problem 7: Race conditions
Consider the following code snippet:
if (!stat("file.dat", buf)) return; // abort if file exists
sleep(10); // sleep for 10 seconds
fp = fopen("file.dat", "w" ); // open file for write
fprintf(fp, "Hello world" );
close(fp);
- Suppose this code is running as a setuid root program. Give an example of how this code can lead to unexpected behavior that could cause a security problem. Hint: see lecture 5 slide 19.
- Suppose the sleep(10) is removed from the code above. Could the problem you identified in part (a) still occur? Please explain.
-
How would you fix the code to prevent the problem from part (a)?
Hint: look up the meaning of the flags O_CREAT and O_EXCL given as arguments to the open Unix system call.
Problem 8: Setuid
You're auditing a new webserver and find the following code snippet:
if (fork() == 0) {
int socket = socket(":80");
if (socket == -1) {
perror("unable to open socket: ");
exit(-1);
}
seteuid(100);
serve(socket);
}
- How can an attacker escalate privileges if there's a bug in the serve function? You can assume that the service account www-data has the UID 100 and exists, and that the process initially is executed as the root user.
- What change can be made to the code to prevent this privilege escalation vulnerability?